How to Select the Right Bus Bar Connectors for UAE & GCC Climates
Look inside any complex electrical system—whether it’s a skyscraper in Dubai or a massive industrial plant in Saudi Arabia—and you’ll find an unsung hero managing the flow of power: the bus bar connector. In the demanding climate of the GCC, selecting the right connector is critical for ensuring safe, reliable power distribution and avoiding costly system failures.
The Hidden Backbone of Your Electrical System

In the high-stakes world of power distribution, bus bar connectors are the foundation of any reliable electrical network. Their job seems simple: create secure, low-resistance joints between busbars, or between a busbar and a cable. But this task is absolutely critical for efficient and safe power flow through switchgear, panel boards, and other key electrical components UAE projects rely on.
Think of a busbar as a major artery carrying electrical current. Without strong, reliable connections, that power can't reach the smaller vessels of the system. A weak or poorly made connection is like a blockage, creating a point of high resistance that chokes the flow.
The Consequences of a Weak Connection
Here in the GCC, the tough operating environment amplifies the risk of a bad connection. High ambient temperatures mixed with heavy electrical loads put immense stress on every single component. A faulty connector can quickly snowball into serious problems:
- Overheating and Hot Spots: High resistance at the connection point generates a ton of heat. This creates a "hot spot" that can melt insulation, damage nearby components, and become a major fire hazard.
- Voltage Drops: An inefficient connection causes the voltage to drop, meaning less power gets delivered to your equipment. This can trigger performance issues, cause machinery to malfunction, or even shut down sensitive industrial processes entirely.
- Catastrophic Failure: In the worst-case scenario, a poorly chosen or badly installed connector can lead to arcing, short circuits, and a total system failure. The result? Costly downtime and serious safety risks.
A bus bar connection is only as strong as its weakest link. For engineers and panel builders in Dubai and Abu Dhabi, choosing high-quality connectors isn't just about following the rules; it's fundamental to ensuring system integrity, safety, and operational continuity.
This is exactly why seasoned professionals across the region insist on robust, properly rated bus bar connectors from trusted suppliers like GoSwitchgear. Picking the right component guarantees the entire electrical assembly can handle the thermal and electrical stresses common in our local industrial and commercial environments. It’s about safeguarding your investment and ensuring reliable performance for years to come.
Decoding the Different Types of Bus Bar Connectors
Choosing the right bus bar connectors is more than just a box-ticking exercise; it's a foundational step for any safe and efficient electrical system. The decision you make here will echo through the system's performance, lifespan, and how easy (or difficult) it is to maintain down the line.
At a high level, connectors are split into two main camps based on how they're installed: mechanical and compression. Getting a handle on the core differences between these two is crucial for any engineer or technician, especially on projects across the UAE and KSA where conditions can be demanding.
Mechanical connectors, which you'll often see in switchgear and panel boards, are the workhorses of the industry. These are your bolted and clamped types, using hardware like bolts, nuts, and pressure plates to physically lock down a secure electrical joint. Their biggest plus? They can be taken apart. This reusability makes them a fantastic choice for systems that might need maintenance or future upgrades.
Compression connectors, on the other hand, are a one-and-done deal. Think of lugs that are permanently crimped onto a busbar or cable using a specialized tool. This process creates a single, solid mass that offers incredible conductivity and strength. But once it's on, it's on for good—you'd have to destroy the connector to remove it.
Core Connector Categories for Your Application
Beyond just how they're installed, bus bar connectors are built for very specific jobs within an electrical assembly. Each type is designed to solve a particular problem, whether it's terminating massive cables or dealing with the physical stresses on long busbar runs.
- Lug Connectors (Cable Terminations): These are probably the most familiar type. Their job is simple but vital: terminate a cable and attach it firmly to a busbar. They typically come in one-hole or two-hole designs to stop them from twisting and ensure a rock-solid connection, even under heavy load.
- Tap-Off Connectors (Branch Circuits): Ever need to pull power for a smaller circuit from a main busbar without cutting into it? That's where a tap-off connector shines. It clamps right onto the main bar, giving you a secure point to feed power to other components.
- Expansion Connectors (Thermal Management): In the intense heat of the GCC, metal expands. As busbars heat up, they grow in length, and this movement can put a huge strain on the system. Expansion connectors are engineered with flexible, often braided, copper shunts that absorb this thermal expansion, preventing stress from wrecking the busbars or their supports.
This diagram helps visualize how different bus bar types are grouped based on their physical makeup and how they're used.
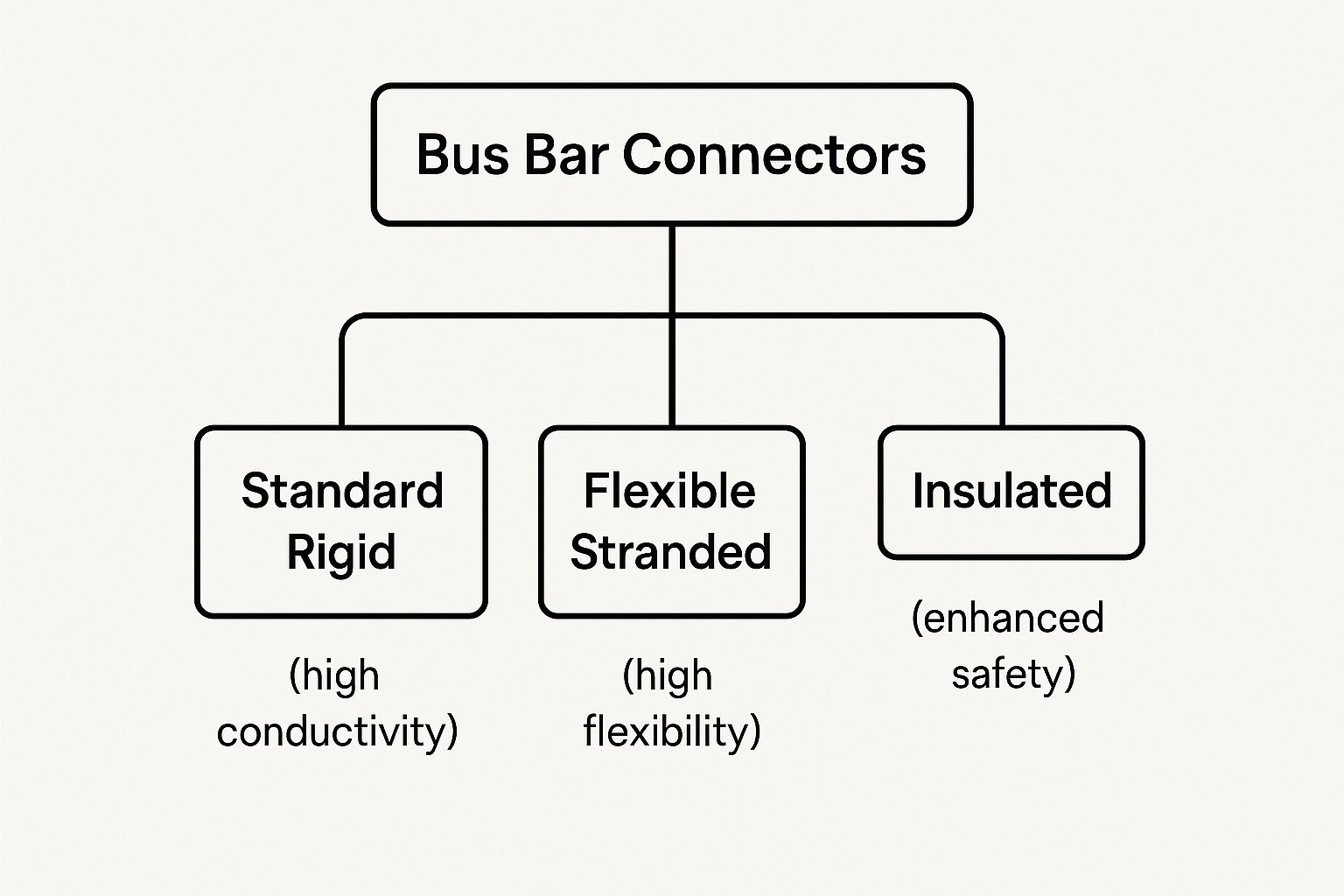
As the chart shows, your initial choice between rigid, flexible, or insulated bus bars will point you toward the specific kind of connector needed to build a safe and effective system.
Mechanical vs. Compression: A Closer Look
So, how do you choose between mechanical and compression? It really boils down to the specific job, the environment it will live in, and your long-term plans for the system. Both are fantastic when used correctly, but they serve different masters. For a project in Dubai where you're already planning for future expansion, mechanical connectors give you that much-needed flexibility.
Here’s a quick breakdown to help you decide:
Mechanical Connectors (Bolted/Clamped)
- Best For: Field installations, systems that will need future maintenance or disassembly, and connecting different busbar sizes.
- Advantages: They're reusable, easy to install with standard tools (like a good torque wrench), and incredibly versatile.
- Considerations: You have to get the torque just right to create a low-resistance connection. It's also a good idea to schedule periodic torque checks, especially in high-vibration areas.
Compression Connectors (Crimped)
- Best For: Permanent installations where you need maximum reliability and resistance to vibration, like in transportation or heavy industrial machinery.
- Advantages: This method creates a super strong, low-resistance, and gas-tight connection that stands up exceptionally well to vibration and thermal cycling.
- Considerations: Installation requires specialized and often pricey crimping tools. The connection is permanent, and once it's made, you can't easily inspect it internally.
For any high-current application, the quality of the connection interface is paramount. A properly installed compression connector creates a near-perfect metallurgical bond, while a correctly torqued mechanical connector provides a reliable and serviceable joint. The choice depends on balancing permanence with serviceability for your specific project needs.
Ultimately, whether you're specifying an energy management solution Dubai depends on or building panels for an industrial site in Saudi Arabia, getting the connector choice right is critical. It's the key to ensuring the electrical components UAE projects are built on will perform reliably for years to come, even under the toughest conditions.
Choosing the Right Connector for GCC Environments
When you're specifying bus bar connectors for a project in the UAE or anywhere in the GCC, it’s not your standard, run-of-the-mill task. The region throws a unique set of challenges at electrical systems: relentless high heat, corrosive humidity, and a constant barrage of fine, abrasive dust. A connector that works just fine in a milder European climate could easily fail prematurely in a Dubai substation or a Saudi industrial plant.
This is why experienced engineers and procurement teams know to look past the generic datasheets. You have to dig deeper, focusing on specifications that scream long-term reliability. The real goal isn't just to build a system that works on day one, but one that keeps running safely and efficiently for decades to come. And it all starts with picking the right connector.
Material Compatibility and Plating Quality
The bedrock of a solid connection lies in material science. While you'll see both copper and aluminum busbars in the field, you have to be incredibly careful about how you connect them. Slapping a standard copper connector onto an aluminum busbar without the right precautions is an open invitation for galvanic corrosion. This destructive process gets supercharged by the salty, humid air common in coastal cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi.
That’s where bimetallic connectors become absolutely critical. They act as a stable, safe bridge between the two different metals. Just as important is the quality of the connector's plating.
- Tin Plating: This is the industry go-to, and for good reason. Tin offers fantastic corrosion resistance and stops that insulating oxide layer from forming on the surface, which is key to maintaining a low-resistance joint over the long haul.
- Silver Plating: For your most critical, high-current applications, silver is the premium choice. It delivers superior conductivity and even better resistance to oxidation. When performance and reliability are non-negotiable, this is the way to go.
In the punishing environment of the GCC, high-quality plating isn't a nice-to-have; it's a must-have. Think of it as a shield, protecting the conductive material from the salt and humidity that can quickly eat away at an unprotected connection point.
Critical Performance Ratings
Moving beyond materials, three performance ratings are the real gatekeepers that determine if a connector is right for the job. For any panel builder or system integrator, these are non-negotiable checks.
First up is the current rating (amperage). It absolutely must meet or, even better, exceed the maximum current the busbar will ever carry. An undersized connector is just a ticking time bomb, waiting to become a dangerous hot spot. Second, the voltage rating has to be right for the system to ensure there’s enough insulation to prevent arcing.
Lastly, and this one is crucial for safety, is the short-circuit withstand capacity. This metric tells you if the connector can hold itself together—mechanically and electrically—during a massive fault. It’s what prevents a catastrophic failure when the system is under the most extreme stress imaginable.
Environmental Protection and Thermal Management
Let's face it, the inside of a panel board in the UAE is a harsh place to be. Dust is everywhere, and ambient temperatures can be scorching. This makes the Ingress Protection (IP) rating of any shrouds or enclosures around the connection incredibly important. You'll want to look for a higher rating, like IP54 or more, to be sure that dust can't get in and mess with the connection.
At the same time, you have to manage the heat. The connectors and busbars generate their own heat, and the high ambient temperatures in the region only make things worse by lowering the current-carrying capacity of every component. This is why proper panel ventilation is vital. If you want to dive deeper into cooling strategies, our detailed guide on selecting the right panel cooling fan is a great resource.
Taking a proactive approach to heat ensures your connectors stay within their designated temperature limits, which is key to preventing premature aging and failure.
To give you an idea of the scale, the Middle East and Africa busway market—which includes the systems that bus bar connectors are a part of—was valued at around USD 737.5 million and is expected to hit USD 1,188.16 million by 2032. This explosive growth shows just how much is being invested in reliable power distribution to keep up with rising energy demands.
By carefully working through these material, performance, and environmental factors, you can confidently choose bus bar connectors that don't just meet local standards from utilities like DEWA but are truly built to thrive in the demanding GCC climate.
Before finalizing your selection, running through a quick checklist can help ensure all bases are covered, especially for the unique conditions in the Gulf.
Bus Bar Connector Selection Checklist for GCC Applications
| Parameter | Specification to Check | Importance in GCC Climate (High/Medium/Low) | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material & Plating | Bimetallic compatibility (if needed), Tin or Silver plating thickness and quality | High | Prevents galvanic corrosion accelerated by high humidity and saline air. |
| Current Rating | Must exceed maximum system amperage. | High | High ambient temperatures derate current capacity; extra margin is crucial. |
| Short-Circuit Rating | Withstand capacity (kA) appropriate for the specific point in the network. | High | Ensures mechanical and electrical integrity during fault conditions to prevent catastrophic failure. |
| Operating Temperature | Maximum rated operating temperature. | High | Must handle high ambient temperatures plus heat generated by the load without degrading. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Salt spray test results, material specifications. | High | Protects against degradation from salt-laden coastal air common in the UAE and GCC. |
| Vibration Resistance | Mechanical strength and locking mechanism. | Medium | Important for industrial plants or applications near heavy machinery to prevent loosening. |
| IP Rating (for Shrouds) | Minimum IP54 recommended. | High | Protects connection points from fine, conductive dust which is prevalent in the region. |
Using a systematic checklist like this one helps you move beyond a simple component choice and towards engineering a truly resilient and long-lasting electrical system tailored for the region.
A Practical Guide to Flawless Connector Installation
Even the best bus bar connectors on the market will fail if they aren’t installed with care. For electricians and technicians working across the UAE, getting the installation right isn't just about following a manual. It’s about creating a rock-solid, low-resistance connection that guarantees safety and peak performance for years to come.
This guide breaks down the essential steps for a reliable connection, from prepping the surfaces to that final turn of the wrench. Getting this right prevents the most common—and dangerous—failure points, ensuring the integrity of your entire electrical assembly. This level of detail is more important than ever, given the region's booming power infrastructure.
In fact, the Middle East and Africa busbar market is projected to hit USD 869.04 million by 2028, growing at a solid 4.2% CAGR. Massive projects in Saudi Arabia and the UAE are driving this growth, which means mastering installation is critical to support these new systems. You can dive deeper into the research on the MEA busbar market growth.
Step 1: Surface Preparation Is Non-Negotiable
The journey to a perfect connection starts before you even pick up a tool. The contact surfaces of both the busbar and the connector have to be perfectly clean. It’s a simple fact: over time, conductive metals like copper form a thin oxide layer. This layer is an insulator, and it will kill your connection by jacking up the electrical resistance.
Here’s how to guarantee a clean, metal-to-metal contact:
- Gently Abrade: Grab a fine-grade, non-metallic abrasive pad or a wire brush. The key is to be gentle. You just want to remove that dull oxide layer until you see bright, shiny metal. Remember to use a stainless steel brush for both copper and aluminum to avoid cross-contamination.
- Wipe Clean: As soon as you're done abrading, wipe the surface with a lint-free cloth and an approved, non-residue solvent. This gets rid of any dust, grease, or leftover metal particles.
- Apply an Inhibitor: This is a must for aluminum connections but also a great practice for copper. A thin layer of jointing compound (oxide inhibitor) fills in microscopic gaps and seals the connection from air and moisture, preventing oxidation from creeping back in.
Step 2: Achieving the Correct Torque
When it comes to bolted bus bar connectors, hitting the correct torque is probably the single most critical step. It’s a fine line to walk—too loose or too tight, and you're setting the stage for catastrophic failure. A calibrated torque wrench isn't a "nice-to-have" here; it's essential.
- Under-Tightening: This is the classic mistake. A bolt that isn't tight enough fails to create the clamping force needed, leaving a high-resistance gap. That gap generates heat, creating a hot spot that can melt insulation, wreck components, and become a serious fire hazard.
- Over-Tightening: Putting too much muscle into it is just as bad. You can stretch the bolt past its elastic limit, damaging it for good. It can also warp the softer metal of the connector or busbar, which ironically leads to a poor connection and eventual mechanical failure.
Expert Tip: Always, always follow the manufacturer's specified torque values for the exact hardware you're using. Don't guess or go by "feel." Your torque wrench is your best friend.
Step 3: Using Hardware Correctly
The nuts and bolts you use play a huge part in keeping the connection solid over the long haul. In the GCC, where temperatures swing, Belleville washers are especially important. These are cone-shaped spring washers, and they're your secret weapon against thermal cycling.
As the busbar heats up under load and cools down, it expands and contracts. This tiny movement can cause bolted connections to loosen over time. A Belleville washer acts like a heavy-duty spring, maintaining constant pressure on the joint through every cycle. This keeps the connection tight and secure, preserving that critical low-resistance path—the kind of reliability an energy management solution Dubai projects rely on.
Don't forget the flat washers, either. They need to be placed correctly to spread the load evenly and stop the bolt head or nut from digging into the connector's surface. It’s the small details that make all the difference.
Proactive Maintenance and Troubleshooting Strategies
When it comes to your electrical system's long-term health, waiting for something to break is a recipe for disaster. Real reliability comes from proactive maintenance, not reactive repairs.
For any facility manager or maintenance engineer, especially in the demanding environments of the UAE and the broader GCC region, a solid inspection strategy for bus bar connectors is non-negotiable. It's what stands between smooth operations and costly, unplanned downtime.
A robust maintenance plan goes far beyond a quick visual once-over. It means bringing in advanced diagnostics to spot trouble long before it becomes a full-blown failure. This is absolutely fundamental to protecting the critical electrical infrastructure that powers facilities across the region every single day.
To keep your bus bar connectors and the entire electrical system performing at their best, you need clear strategies in place. For a wider view, learning how to troubleshoot common electrical problems is a great addition to any comprehensive asset management plan.
Creating an Effective Inspection Schedule
Your routine inspection schedule is the backbone of any preventative maintenance program. For any piece of critical infrastructure, this needs to happen at least once a year—no exceptions.
Your plan should be built around a few key actions:
- Detailed Visual Checks: Get up close and look for any signs of overheating. This often shows up as discoloration on the connector itself or melted insulation on nearby cables. Also, check for any physical signs of corrosion, which is a major concern in our humid and saline coastal environments.
- Thermographic Scanning: This is your most powerful tool. Using an infrared camera, a technician can scan all your bus bar connections while they're under load. This allows you to spot "hot spots" that are completely invisible to the naked eye. Any connection that's significantly hotter than its neighbors is a clear red flag for a high-resistance joint that needs attention—fast.
- Periodic Torque Verification: Bolted connections aren't "set it and forget it," especially in facilities with heavy machinery or big temperature swings. Vibrations and thermal cycling can cause connections to loosen over time. A periodic check with a calibrated torque wrench ensures that clamping force stays exactly where the manufacturer specified, stopping a high-resistance fault from ever developing.
A Practical Troubleshooting Guide
When you do find an issue, a systematic approach is the only way to get to the root cause quickly. High-resistance joints and intermittent connections are, by far, the most common culprits.
Here’s a simple framework to follow:
| Symptom | Potential Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Spot Detected | A loose connection from insufficient torque, surface oxidation, or the wrong hardware. | De-energize the circuit. Disassemble the connection, clean the contact surfaces thoroughly, replace any suspect hardware, and re-torque to the correct spec. |
| Intermittent Power | A loose connection, likely caused by vibration or thermal cycling. | Inspect closely for any signs of movement or electrical arcing. Tighten the connection and consider adding Belleville washers to maintain consistent pressure. |
| Visible Corrosion | A galvanic reaction (like copper touching aluminum) or harsh environmental factors. | Replace the connector with one made of the right material (e.g., a bimetallic connector). Clean the busbar and apply an oxide inhibitor before putting it all back together. |
A hot connection is a failing connection. Thermography lets you see these failures developing long before they lead to a catastrophic event, making it an essential investment for any facility manager in Dubai or Abu Dhabi.
This proactive approach doesn't just extend the life of your equipment; it builds a culture of safety. The foundation of that culture is proper training. For teams looking to sharpen their skills, dedicated electrical safety training provides the crucial knowledge needed to perform these tasks safely and effectively.
Ultimately, taking care of your bus bar connectors is about safeguarding your entire operation from the ground up.
Connectors in Action Across the UAE and Saudi Arabia
You can talk theory all day, but the real test of a bus bar connector is out in the field. This is especially true in the high-stakes, demanding environments you find all over the UAE and Saudi Arabia. From hyper-critical data centers in Dubai to sprawling shopping malls in Riyadh, these components are the unsung heroes making sure the power stays on. Their performance isn't just a technical footnote; it's a vital part of what makes the region's most ambitious projects successful.
The numbers don't lie. The Middle East and Africa busbar trunking market, which depends entirely on top-tier connectors, pulled in USD 606.5 million and is on track to hit USD 935.4 million by 2033. This isn't just growth; it's a clear signal that the demand for reliable, tough-as-nails components is skyrocketing.
Mission-Critical Data Centers
In a data center, uptime isn't just important—it's everything. A single millisecond of power loss can mean catastrophic data loss and huge financial hits. It’s no surprise, then, that bus bar connectors here are picked for one thing above all else: absolute, unquestionable reliability.
- Requirement: The connections have to be incredibly stable, with low resistance to keep heat generation to a minimum in those tightly packed server racks.
- Solution: You’ll almost always see high-quality compression lugs and bolted connectors with silver plating. This isn't for show; it ensures maximum conductivity and stops any performance drop-off over the years.
Large-Scale Commercial and Retail Projects
Picture the immense electrical demands of a place like the Dubai Mall or one of the new mega-entertainment complexes in KSA. These buildings run on complex power distribution networks that have to power everything from massive HVAC systems to thousands of lights.
- Requirement: The electrical system must be flexible enough to accommodate future tenants and expansions, all while handling constant, heavy loads without a hiccup.
- Solution: This is where mechanical bolted connectors shine. They make maintenance and system modifications much simpler down the road. In the region's humid climate, bimetallic connectors are also a must-have wherever aluminum and copper busbars meet to head off corrosion. Getting these systems right is a huge undertaking, which is why specialized expertise from firms providing MEP engineering services in Dubai is so critical for effective integration.
In landmark projects across the GCC, the selection of every component, including bus bar connectors, reflects a commitment to quality and long-term performance. Partnering with a trusted supplier like GoSwitchgear ensures that the specified components meet the rigorous demands of these iconic structures.
Vital Public Infrastructure
Think about the lifelines of a modern city: airports, metro systems, and hospitals. The electrical components UAE infrastructure depends on have to deliver unwavering performance and safety. A single failed connection here isn't an inconvenience; it's a direct threat to public safety and transport.
- Requirement: Connections must be tough enough to handle constant vibrations from trains or heavy machinery and operate perfectly for decades.
- Solution: Only connectors with superior short-circuit ratings and excellent vibration resistance will do. These are often secured with Belleville washers for an extra layer of security. Of course, these components are just one piece of a much larger safety puzzle that includes a full suite of robust electrical protection equipment to protect the entire network.
Common Questions About Bus Bar Connectors
When it comes to specifying or installing bus bar connectors, engineers, technicians, and even procurement teams across the GCC often have some very specific questions. Getting the right answers is non-negotiable for project safety and long-term reliability.
Let's tackle some of the most common queries we hear, so you can feel confident making decisions for your next project in the UAE or KSA.
Why Is Applying the Correct Torque So Important for Bolted Connectors?
Think of torque as the "magic ingredient" for a solid electrical connection. It’s absolutely critical because it creates the precise clamping force needed for a low-resistance joint. If a connection is under-torqued (too loose), you're creating a high-resistance point. This leads to dangerous heat buildup, wasted energy, and a serious fire risk.
On the flip side, if you over-torque it (too tight), you can stretch the bolt past its elastic limit, deform the connector, or even crack the busbar itself. That’s a recipe for a catastrophic mechanical failure. The only way to get it right is to use a calibrated torque wrench and follow the manufacturer's exact specifications. It’s the only path to a safe, efficient, and durable connection.
Can I Connect an Aluminum Bus Bar Directly to a Copper Connector?
Connecting aluminum directly to copper is a classic mistake and one you really want to avoid, especially in the humid and salty environments common in the GCC. When these two metals touch, they kick off a process called galvanic corrosion. It's an electrochemical reaction that literally eats away at the connection point.
This corrosion doesn't just look bad; it dramatically increases electrical resistance, which generates heat and eventually causes the entire joint to fail.
The right way to join these dissimilar metals is by using a bimetallic connector or a specially designed bimetallic washer. These are engineered with bonded layers of aluminum and copper, creating a stable bridge that stops corrosion in its tracks and ensures the connection stays solid for the long haul.
How Often Should Bus Bar Connections Be Inspected in a Dubai Facility?
For any critical facility, especially one dealing with the demanding climate in Dubai, a full inspection should happen at least once a year. This isn't just a quick glance. A proper annual check involves a detailed visual inspection for any obvious signs of trouble like discolouration (a tell-tale sign of overheating) or physical corrosion.
More importantly, it must include a thermographic scan using an infrared camera. This lets you spot "hot spots" that are completely invisible to the naked eye. For facilities with extremely heavy electrical loads, high ambient temperatures, or a lot of vibration, bumping that inspection schedule up to every six months is a smart move for safety and operational reliability.
What Are Belleville Washers and When Should I Use Them?
Belleville washers are clever, cone-shaped springs that act like heavy-duty lock washers in electrical systems. Their main job in a bus bar connection is to maintain constant pressure on the joint, even when it expands and contracts with temperature changes—a process we call thermal cycling.
You'll definitely want to use them in any application with fluctuating loads or big temperature swings. By continuously applying that clamping force, Belleville washers keep the bolted connection from loosening over time. This guarantees a secure, low-resistance joint that you can count on for its entire service life. They are a small component that makes a huge difference in reliability.
For access to a complete range of high-quality bus bar connectors and expert support for your projects in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and across the GCC, explore the extensive catalogue from GoSwitchgear.
Find the Right Electrical Components for Your Project at GoSwitchgear









Leave a Reply