Your Guide to Selecting and Installing a DOL Motor Starter in the UAE
A DOL (Direct-On-Line) motor starter is the simplest and most cost-effective method for operating a three-phase induction motor. As its name implies, it connects the motor directly to the full power line voltage, delivering maximum starting torque instantly. This straightforward design has made it a fundamental component in countless industrial and commercial applications across the UAE and the wider GCC region.
Why a DOL Starter Is Essential for UAE Projects
In the demanding industrial environments of the UAE—from Dubai's manufacturing hubs to Abu Dhabi's large-scale infrastructure projects—engineers and panel builders require solutions that are robust, simple, and economical. For small to medium-sized motors, the Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter is consistently the preferred choice, offering a reliable control method that stands up to local challenges.
Its primary strength lies in its uncomplicated design. By applying full line voltage directly to the motor terminals, it provides immediate, high torque without complex electronics. This makes the DOL motor starter an indispensable workhorse for powering essential machinery throughout the GCC.
Built for Demanding Environments
The UAE and GCC climate presents significant challenges for electrical equipment, including high ambient heat, humidity, and pervasive dust. These conditions can compromise sensitive electronic components, but the rugged, electromechanical construction of a DOL starter ensures reliable performance. This inherent resilience makes it ideal for:
- HVAC Systems: Ensuring reliable operation of fans and compressors, even during peak summer temperatures.
- Water Pumping Stations: Maintaining a consistent, uninterrupted flow for water supply and irrigation.
- Workshop Machinery: Providing dependable power for drills, lathes, and grinders in industrial settings.
- Small Conveyor Systems: Driving material handling equipment in warehouses and manufacturing facilities.
For project managers and procurement teams in Dubai or across the GCC, the reliability of a DOL starter translates directly to reduced downtime and lower maintenance costs. Its ability to perform consistently in harsh conditions is a key reason for its widespread use.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the DOL motor starter, covering its operation, component selection, and installation best practices tailored for professionals in the UAE. Mastering these fundamentals is essential for building motor control systems that are both efficient and safe.
How a DOL Motor Starter Works & Its Core Components
A DOL motor starter functions as an intelligent, heavy-duty switch designed to handle the significant power demands of industrial motors. Its operation is brilliantly simple, relying on a few core components to deliver power reliably while protecting the motor from electrical faults. For any panel builder or engineer in the UAE, understanding the interaction between these parts is fundamental.
The system comprises two distinct circuits: the power circuit, which carries the high-voltage current directly to the motor, and the control circuit, a low-voltage system that governs when the power circuit is energized based on operator commands and safety inputs.
The Contactor: The Main Power Switch
The central component is the magnetic contactor, a powerful relay engineered to handle the large inrush current a motor draws upon starting. When the 'Start' button is pressed, a small current energizes the contactor's internal coil.
This current generates a magnetic field that closes a set of heavy-duty contacts, completing the power circuit and applying full line voltage to the motor. A wide range of contactors, such as those in our GoSwitchgear Schneider Electric contactor catalogue, are built to withstand tough industrial environments.
A latching or holding circuit utilizes an auxiliary contact to keep the coil energized after the 'Start' button is released, ensuring the motor continues to run until the 'Stop' button is pressed or a fault is detected.
The Overload Relay: The Motor's Guardian
The most critical safety device in a DOL starter is the thermal overload relay (OLR). Its sole function is to protect the motor from damage caused by overcurrent conditions. This protection is especially vital in the high ambient temperatures of the GCC, where motors operate closer to their thermal limits.
The OLR employs a bi-metallic strip that heats up and bends when excess current passes through it. If the overload persists, the strip bends sufficiently to trip a switch in the control circuit. This action instantly de-energizes the contactor coil, causing the main power contacts to open and shut down the motor, preventing a costly burnout.
The Control Interface: Start and Stop Push Buttons
The operator interacts with the starter through a simple interface of start and stop push buttons.
- Start Button (Normally Open): Pressing this green button completes the control circuit, energizes the contactor coil, and starts the motor.
- Stop Button (Normally Closed): Pressing this red button breaks the control circuit, de-energizing the coil and stopping the motor.
This infographic summarizes why this simple, reliable, and cost-effective configuration is so widely adopted.
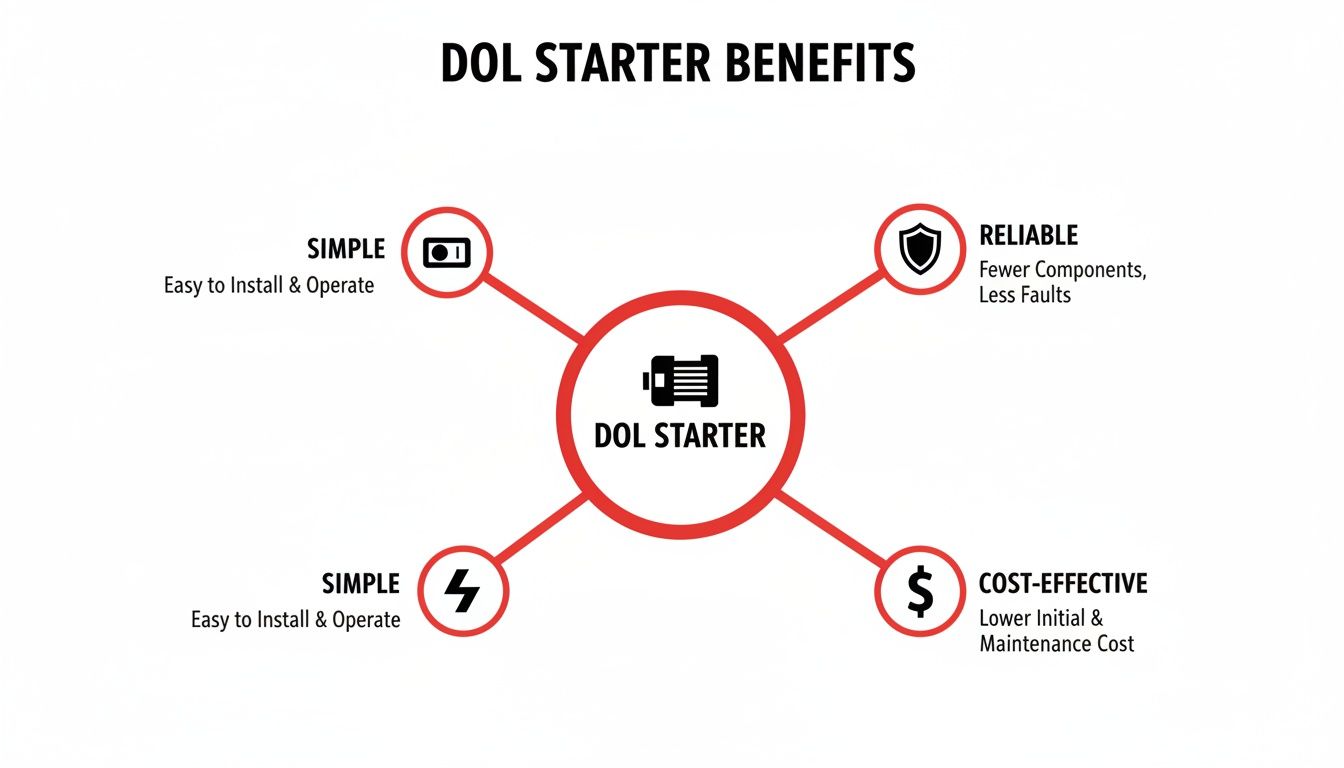
As shown, the design's simplicity translates directly to high reliability and lower project costs—two critical factors for any project in the region. The electromechanical nature of the DOL motor starter makes it the preferred choice for countless applications where failure is not an option.
Choosing the Right DOL Starter for Your Application
Selecting the correct DOL motor starter involves more than matching a kilowatt (kW) rating. For engineers, electricians, and procurement managers in the UAE, proper selection is critical for operational safety, reliability, and motor longevity. This decision directly impacts performance, particularly within the challenging climate of the GCC.
The process requires careful consideration of the motor's characteristics and its operating environment. Correct selection prevents nuisance tripping, avoids motor failure, and ensures compliance with local standards. Let's review the essential steps for making an informed decision.
Step 1: Start with the Motor Nameplate
The motor's nameplate provides the most critical information for sizing the starter components. Always refer to the specific motor's data rather than relying on generic charts.
The key value is the Full Load Current (FLC), or 'Rated Current'. This figure, in amperes (A), indicates the current the motor is designed to draw at its full rated power and is the basis for all subsequent calculations.
Step 2: Select the Contactor Rating
With the FLC determined, the next step is to choose the main contactor. The contactor must handle not only the continuous running current but also the stress of repeated starting and stopping cycles.
- Look for the AC-3 Rating: This IEC standard is specifically for switching squirrel-cage induction motors. It certifies that the contactor can handle the high inrush currents associated with motor starts.
- Build in a Safety Margin: Best practice is to select a contactor with an AC-3 rating at least 25% higher than the motor’s FLC. For a motor with a 20A FLC, a contactor rated for at least 25A (AC-3) is recommended. This provides a buffer for voltage fluctuations and demanding regional conditions.
Step 3: Configure the Thermal Overload Relay
The thermal overload relay is the motor's primary defense against overcurrent damage. Correctly setting this device is non-negotiable for safety. An incorrect setting can either expose the motor to burnout or cause unnecessary shutdowns.
The standard and safest practice is to set the overload relay dial to 115%–125% of the motor's FLC. For a motor with a 10A FLC, the setting should be between 11.5A and 12.5A. Exceeding this range defeats its protective purpose.
Step 4: Consider Environmental Factors in the UAE and GCC
The environment in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and across the Gulf significantly impacts component selection, especially the enclosure.
- Heat Derating: High ambient temperatures reduce the ability of components to dissipate heat. Check manufacturer datasheets for derating factors if the starter will operate in environments exceeding 40°C.
- Enclosure IP Rating: The enclosure protects internal components. For dusty environments like construction sites or workshops, a minimum IP54 rating is required. For outdoor installations or areas exposed to water spray, an IP65 rating is necessary.
This reference table provides guidance for common motor sizes found in the UAE. Always verify against the motor's actual nameplate data.
DOL Starter Selection Guide for Common Motor Ratings in the UAE
This table offers a starting point for selecting components for standard three-phase induction motors.
| Motor Power (kW) | Typical Full Load Current (FLC) at 400V (Amps) | Recommended Contactor AC-3 Rating (Amps) | Overload Relay Setting Range (Amps) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 kW | 3.4 A | 9 A | 3.9 A – 4.3 A |
| 2.2 kW | 4.7 A | 9 A | 5.4 A – 5.9 A |
| 4.0 kW | 8.1 A | 12 A | 9.3 A – 10.1 A |
| 5.5 kW | 11.0 A | 18 A | 12.7 A – 13.8 A |
| 7.5 kW | 15.0 A | 25 A | 17.3 A – 18.8 A |
By following these steps, you can ensure your DOL motor starter is correctly matched to its application. For further details on wiring, explore three-phase motor connections in our detailed guide. This methodical approach ensures a safe, reliable, and efficient installation.
Best Practices for DOL Starter Wiring and Installation
Proper installation is fundamental to the safety, reliability, and longevity of a DOL motor starter. For electricians and panel builders in the UAE, correct wiring is non-negotiable, preventing operational failures, protecting motors, and ensuring compliance with local standards.
The process involves respecting the distinction between the high-voltage power circuit and the low-voltage control circuit. Achieving perfect harmony between these two systems is the objective of a professional installation.

Differentiating Power and Control Circuits
Maintaining separation between power and control circuits is a core principle of safe panel building.
- The Power Circuit: This circuit uses heavy-gauge wiring to carry the full motor current from the incoming three-phase supply (L1, L2, L3), through a circuit breaker, the contactor's main terminals (1, 3, 5), the overload relay (2, 4, 6), and finally to the motor (U, V, W).
- The Control Circuit: This low-power system energizes the contactor's coil. It typically uses a single phase, passing through the stop button (NC), start button (NO), and the overload relay's auxiliary contact (NC) before reaching the contactor coil (A1). The other side of the coil (A2) is connected to another phase or neutral.
A correctly wired starter ensures these two circuits are electrically distinct, which is crucial for operator safety and reliable function. Mixing these circuits is a common cause of component failure.
Key Installation Steps and Considerations
A structured installation process minimizes errors and enhances safety. Panel builders in Dubai and Abu Dhabi should standardize this workflow to maintain quality.
- Mounting the Starter: Securely mount the DOL motor starter inside a suitable control panel, allowing at least 50mm of clearance on all sides for ventilation. This is critical in the GCC's high ambient temperatures to prevent overheating and nuisance tripping.
- Cable Sizing and Preparation: Select the correct cable size for both circuits based on the motor's FLC, applying derating factors for heat as required by local regulations. Use a breaker and wire size calculator to verify compliance. Ensure clean insulation stripping and use proper lugs or ferrules for secure connections.
- Terminations and Torqueing: Loose connections are a significant fire hazard due to high resistance and heat generation. Use a calibrated torque screwdriver to tighten all terminals to the manufacturer's specified values. This step dramatically improves long-term reliability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in the UAE
Even experienced electricians can make simple errors that lead to significant problems.
- Incorrect Phase Sequencing: Connecting phases in the wrong order (e.g., L1-L3-L2) will cause reverse motor rotation, which can be catastrophic for pumps or conveyor systems. Always verify motor rotation before commissioning.
- Inadequate Earthing: A reliable earth connection is essential for electric shock protection. Ensure a correctly sized earth wire is securely connected from the main earth bar to both the starter's earth terminal and the motor frame.
- Bypassing the Overload Relay: Never wire the control circuit in a way that bypasses the overload relay's trip contact. This removes the motor's only protection against overcurrent, leaving it vulnerable to burnout.
DOL Starters vs VFDs and Soft Starters
While the DOL motor starter is a reliable workhorse, it is not the only motor control solution. For engineers and project managers in the UAE, selecting the right method involves balancing upfront cost with long-term operational requirements.
The choice typically involves three options: the DOL starter, the soft starter, and the Variable Frequency Drive (VFD). Each has its specific advantages, and understanding their differences is crucial for specifying an effective and economical system.
The Simple Workhorse: DOL Starter
The DOL starter is the most direct and budget-friendly way to start a motor, delivering 100% of its starting torque instantly.
- Best For: Small motors, typically under 10 kW, used in simple applications like workshop tools, small pumps, and fans where high starting current and mechanical shock are acceptable.
- Key Advantage: Unmatched simplicity and low initial cost. It is rugged, easy to troubleshoot, and performs reliably in the harsh conditions of the GCC.
The Smooth Operator: Soft Starter
A soft starter gradually ramps up the voltage during startup, mitigating the main drawbacks of a DOL starter.
- Best For: Applications where sudden mechanical shock would cause damage or where high inrush current must be managed. Examples include conveyor belts, escalators, and centrifugal pumps where a gentle start prevents water hammer.
- Key Advantage: It reduces mechanical wear on gears, couplings, and belts, extending machinery life. It also limits inrush current, preventing voltage dips that can affect other equipment.
The Precision Master: Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)
The VFD is the most advanced option, providing complete control over the motor's speed by adjusting both voltage and frequency.
- Best For: Applications requiring precise speed control, such as variable-flow HVAC systems, advanced pumping stations, and industrial processes where motor speed must match demand.
- Key Advantage: Significant energy savings. By running a motor only as fast as necessary, a VFD can reduce electricity consumption by up to 50% or more. This makes it a powerful tool for reducing operational costs in facilities in Dubai and Abu Dhabi.
For procurement teams, the decision often balances initial capital expenditure against the total cost of ownership. A DOL starter has the lowest upfront cost, but a VFD can offer a rapid return on investment through energy savings.
This table highlights the key differences between these motor control technologies.
DOL Starter vs Soft Starter vs VFD: A Technical Comparison
This table compares features to help you select the best option for your project in the UAE.
| Feature | DOL Motor Starter | Soft Starter | Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lowest | Moderate | Highest |
| Starting Current | Very High (6-8x FLC) | Reduced (Typically 2-4x FLC) | Fully Controlled (Often limited to <1.5x FLC) |
| Mechanical Stress | High (sudden torque application) | Low (gradual torque ramp-up) | Very Low (fully controlled acceleration) |
| Speed Control | None (fixed speed only) | None (controls start/stop only) | Full speed control from zero to max RPM |
| Energy Savings Potential | None | Minimal (only during startup) | Very High (matches motor speed to load) |
| Typical UAE Applications | Small pumps, workshop machines, simple fans & blowers. | Conveyor belts, escalators, centrifugal pumps to prevent hammering. | HVAC systems, large-scale pumping stations, industrial process control. |
Ultimately, the right starting method depends on the application's demands. For simple, fixed-speed tasks, the robust and economical DOL motor starter remains the champion, proving its value in projects across the GCC.
Troubleshooting Common DOL Starter Faults
Even a reliable DOL motor starter can experience faults, leading to costly downtime. For maintenance engineers in the UAE, rapid diagnosis and repair are essential skills, as high ambient temperatures can accelerate component wear. A methodical troubleshooting approach can prevent minor issues from becoming major shutdowns.
This guide provides practical steps to diagnose and resolve the most common problems encountered in the field.

Problem 1: The Motor Fails to Start
When the start button is pressed and nothing happens, the issue is almost always within the control circuit.
- Check Control Circuit Voltage: Use a multimeter to verify that the control circuit is receiving voltage.
- Inspect Push Buttons: Ensure the start button (Normally Open) makes proper contact when pressed and the stop button (Normally Closed) has continuity. Dust, a common issue in the GCC, can impede connections.
- Test Contactor Coil: A burnt-out coil is a frequent failure. With the power off, check the coil's continuity with a multimeter. An open circuit indicates the coil needs replacement.
- Check the Overload Relay: An overload trip will prevent the motor from starting. If it has tripped, investigate the cause before resetting.
Problem 2: The Overload Relay Trips Repeatedly
Constant tripping, or "nuisance tripping," indicates that the motor is drawing excessive current.
Crucial Tip: Never set the overload relay beyond 125% of the motor's FLC as a quick fix. This removes the motor's protection and risks catastrophic failure.
Potential causes include:
- Incorrect Settings: Double-check that the relay is set correctly according to the motor's nameplate FLC.
- High Ambient Temperature: Heat in the UAE increases motor and cable resistance, leading to higher current draw. Ensure the panel has adequate ventilation.
- Mechanical Issues: A blocked pump or seized bearings will force the motor to work harder, causing an overload.
- Unbalanced Power Supply: An unbalanced three-phase supply can cause the motor to draw excessive current. Check the voltage between all three phases.
Problem 3: The Contactor is Humming or Chattering
A loud, buzzing contactor indicates that the electromagnet is not closing properly, which can quickly burn out the coil and damage the contacts.
- Low Coil Voltage: This is the most common cause. Check the control circuit voltage directly at the coil terminals (A1/A2).
- Debris in Assembly: Dust or debris can physically obstruct the contactor's magnetic assembly, preventing it from closing fully.
- Broken Shading Ring: A small copper shading ring on the magnet face prevents humming. If it is broken or missing, the contactor will chatter.
For more information on maintaining industrial equipment, see our guide on efficient industrial equipment repair.
Got Questions About DOL Starters? We've Got Answers.
Our teams in Dubai and Abu Dhabi frequently receive questions about Direct-On-Line starters. Here are answers to the most common queries from technicians and engineers in the UAE.
What's the biggest downside of using a DOL starter?
The primary disadvantage is the high inrush current upon startup, which can be 6 to 8 times the motor's normal running current (FLC).
This current surge can cause a voltage dip on the local electrical network, affecting sensitive equipment. Additionally, the abrupt start imposes significant mechanical stress on the motor's shaft, bearings, and connected machinery like gearboxes. For these reasons, DOL starters are typically used for smaller motors, generally under 10 kW.
Can I use a DOL starter for any three-phase motor?
No, they are not a universal solution. A DOL starter is ideal for small motors driving applications like basic pumps, fans, or compressors, where high starting torque is beneficial and mechanical shock is manageable.
For larger motors or applications requiring a gentle start, such as long conveyor belts or escalators, a soft starter or VFD is a better choice. It is also crucial to consult local utility regulations in the UAE or KSA, as they often impose limits on the maximum motor size that can be started direct-on-line to maintain grid stability.
How do I set the thermal overload relay correctly?
Correctly setting the thermal overload relay is the single most important step in protecting your motor from burnout. First, identify the motor's Full Load Current (FLC) on its nameplate.
Industry best practice is to set the overload relay dial to 115% to 125% of the FLC. For a motor with a 10 Amp FLC, the setting should be between 11.5A and 12.5A. A setting that is too low will cause nuisance tripping, while a setting that is too high will disable its protective function and leave the motor vulnerable.
For expert advice and a complete catalogue of DOL starters and other industrial electrical components in the UAE, the team at GoSwitchgear is ready to assist.
Find the right motor control solution for your project at GoSwitchgear










Leave a Reply