A Guide to Selecting GI Electrical Conduits for Projects in the UAE & GCC
In the demanding climate of the UAE and GCC, your building's electrical wiring is a critical asset that requires robust protection. Think of it as the system's nervous system—complex, vital, and surprisingly fragile. This is where GI (Galvanized Iron) electrical conduits provide the essential backbone, shielding this critical infrastructure from physical impacts, moisture, and fire, ensuring safety and reliability for years to come.
Why GI Conduits Are a Non-Negotiable Choice in the GCC
The UAE and the wider GCC region present a uniquely challenging environment for construction materials. The combination of intense heat, high humidity, and corrosive coastal air means that standard electrical protection simply isn't enough. Engineers, electricians, and project managers across Dubai and Saudi Arabia understand that specifying the right infrastructure is a project-critical decision.
This is precisely why Galvanized Iron (GI) electrical conduits are a mandatory component for any serious commercial or industrial project in the region. These zinc-coated steel pipes serve a dual purpose: providing a tough physical shield against crushing and moisture, and creating a continuous grounded path essential for fault protection and preventing electric shocks.
The Clear Choice for Regional Projects
The market data confirms the trend towards robust, long-lasting solutions. The Middle East and Africa's electrical conduit market was valued at USD 736.2 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% through 2030. Rigid conduits, especially GI, represent the largest and fastest-growing segment, a clear indicator of their importance in the region’s massive infrastructure projects. You can explore this further in the full market analysis on Grand View Research.
For any project, whether in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, or across Saudi Arabia, GI conduits are the go-to solution for several key reasons:
- Extreme Durability: They offer unmatched protection against physical abuse during and after construction, a constant risk on busy job sites.
- Corrosion Resistance: The galvanized zinc coating is crucial, creating a barrier against rust and decay caused by the humidity and salty air common in coastal cities. An essential feature for any electrical components UAE projects require.
- Enhanced Fire Safety: Steel is non-combustible. In a fire, GI conduits help contain the blaze and prevent it from spreading along wiring pathways.
- Regulatory Compliance: Using certified GI electrical conduits is essential to meet the strict safety and quality codes mandated by local authorities like DEWA and ADDC.
When system longevity, crew safety, and regulatory approval are paramount, experienced engineers in the GCC consistently turn to rigid GI conduits. They are the proven solution for the region's most demanding environments.
How to Select the Right GI Conduit for Your Project
Choosing the right GI electrical conduit is a critical decision that directly impacts the safety, lifespan, and compliance of your entire project. A misstep can lead to system failures, costly rework, and significant safety risks, particularly in the harsh environments across the UAE and GCC. A methodical approach, starting with your project's specific demands—mechanical stress, corrosion exposure, and budget—is essential.
Understanding Conduit Classes: Class 3 vs. Class 4
One of the first specifications to consider is the conduit class, which primarily relates to wall thickness and, therefore, its mechanical strength.
- Class 3 GI Conduit: This is a medium-weight option offering solid protection for most commercial and light industrial applications. It balances durability and cost, making it suitable for surface wiring in areas with a low risk of heavy physical impact.
- Class 4 GI Conduit: This is the heavy-duty solution. With a significantly thicker wall, Class 4 provides maximum mechanical protection. It is specified for demanding environments like industrial plants, underground installations, and any area with a high probability of impact, making it the standard for critical infrastructure projects in Dubai and Abu Dhabi.
This image provides a visual overview of common conduit types.
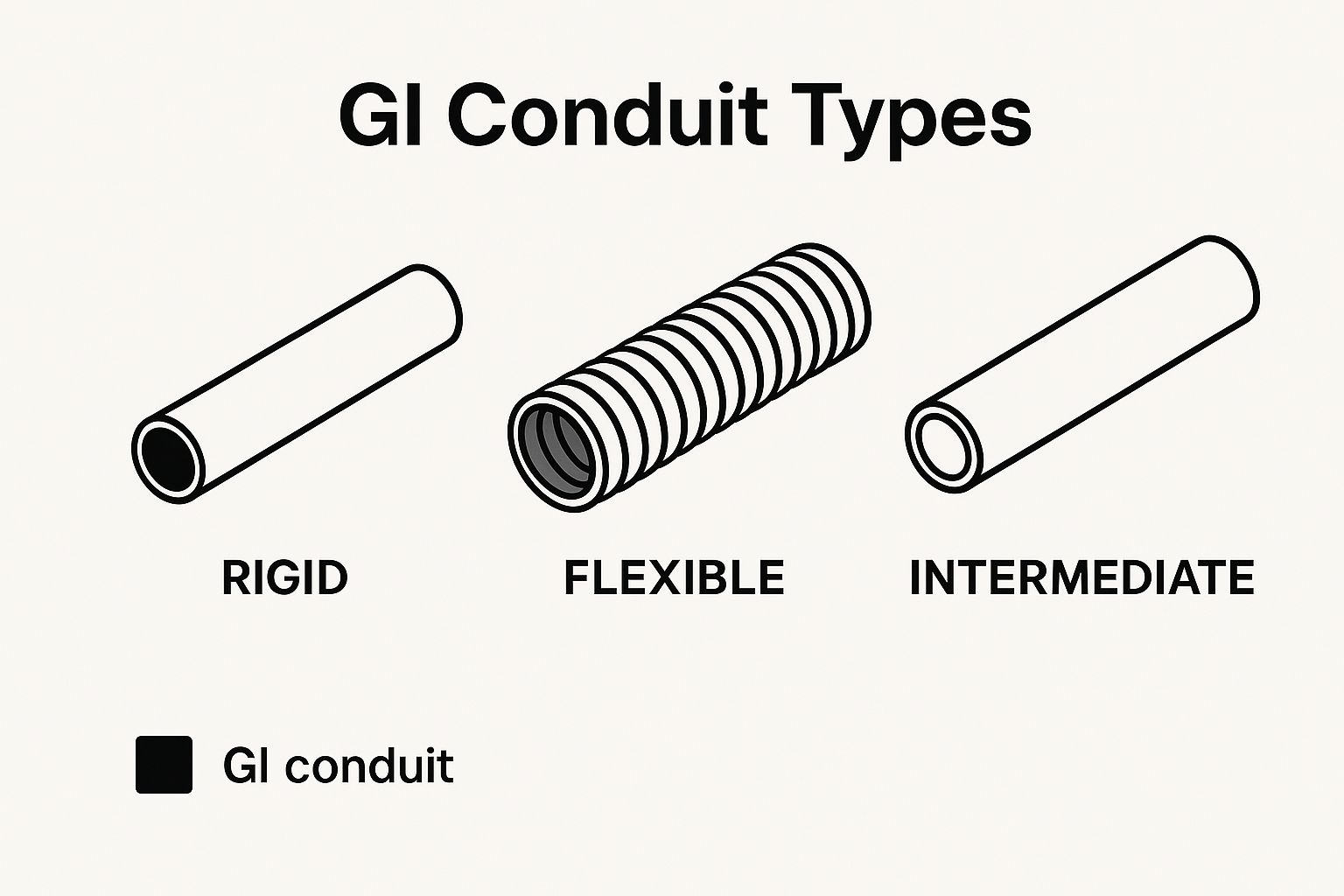
While rigid conduits form the core of most systems, other types offer unique benefits. For complex installations requiring greater adaptability, such as connecting machinery, a flexible electrical conduit may be a more suitable choice.
Comparing GI Conduit Classes for GCC Projects
This table outlines the core features and ideal applications of Class 3 and Class 4 conduits to aid in your decision-making for projects in the GCC.
| Specification | Class 3 GI Conduit | Class 4 GI Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | Medium | Heavy |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | High |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | Very High |
| Best For | Surface wiring in commercial buildings, light industrial areas, and locations with low risk of physical damage. | Heavy industrial environments, underground installations, outdoor applications, and critical infrastructure projects. |
| GCC Application | Ideal for indoor malls, office towers, and residential complexes where the conduit is protected. | The standard for oil and gas facilities, manufacturing plants, and public works projects across the UAE and KSA. |
Ultimately, choosing between Class 3 and Class 4 is a risk assessment: how much abuse will the conduit endure over its service life? The answer will guide your specification.
Comparing Galvanization Methods: Hot-Dip vs. Pre-Galvanized
The galvanization method determines the conduit's resistance to corrosion—a critical factor for projects in the humid, coastal environments of the GCC.
Choosing the right galvanization process is a long-term investment in your electrical system’s integrity. A higher initial cost for better protection often translates to significantly lower maintenance expenses and a longer service life, preventing premature system failure due to corrosion.
There are two primary methods:
- Hot-Dip Galvanization (HDG): The premium choice. The fabricated steel conduit is immersed in a bath of molten zinc, creating a thick, metallurgically bonded coating that covers all surfaces, inside and out. HDG offers superior corrosion protection, making it essential for outdoor, underground, or coastal projects.
- Pre-Galvanization (In-Line): A more economical method where a steel sheet is coated with zinc before being rolled into a conduit. The welded seam and cut ends remain vulnerable to rust over time. It is a suitable option for dry, indoor environments where corrosion is not a major concern.
Meeting Compliance And Standards In The GCC
In the dynamic construction and industrial sectors of the UAE and GCC, adherence to standards is the foundation of safety, asset protection, and long-term system reliability. For GI electrical conduits, navigating the complex web of certifications and local authority regulations is non-negotiable. Using non-compliant materials can lead to project delays, costly rework, and rejection by authorities like DEWA, SEWA, or ADDC.
Core Standards Governing GI Conduits
Two British Standards (BS) are the primary benchmarks for quality that procurement managers and site engineers in the region must know.
-
BS 4568: The established standard for steel conduits, defining classes based on dimensions, screw threads, and protective coatings. A specification for "BS 4568 Class 4" refers to heavy-gauge, hot-dip galvanized conduit designed for maximum mechanical strength.
-
BS EN 61386: The more modern European standard, now widely adopted in the region. It uses a detailed classification system based on performance tests for compression strength, impact resistance, temperature range, and—critically for the GCC—corrosion resistance.
A high compression rating under BS EN 61386, for example, provides assurance that the conduit will not be crushed when embedded in concrete. While GI electrical conduits offer robust protection, some less demanding applications might be better suited for other materials. You can learn more in our guide on PVC electrical conduits and their uses.
Why Corrosion Classification Is King In The GCC
Of all the ratings in BS EN 61386, corrosion resistance is the most critical for projects in the UAE or coastal areas of KSA. The standard uses a scale from 1 (very light protection) to 5 (very high protection).
For any project exposed to the harsh coastal air or high humidity found in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, or Dammam, specifying a conduit with a Class 4 (High) or Class 5 (Very High) corrosion resistance rating is a must. This ensures the zinc coating is thick enough to protect the steel from the relentless attack of salt and moisture.
A hot-dip galvanized finish is the only way to achieve these higher ratings. Opting for a cheaper, pre-galvanized product in an outdoor or marine environment invites premature rust and system failure.
Ensuring Your Supplier And Product Are Compliant
Sourcing your GI electrical conduits from a reputable supplier like GoSwitchgear is your best defense against compliance issues. A reliable supplier provides the necessary documentation to verify product quality.
Here’s a quick compliance checklist:
- Request a Certificate of Conformity: This manufacturer-issued document should clearly state that the product conforms to a specific standard, such as BS EN 61386.
- Check Product Markings: Compliant conduit is permanently marked with the manufacturer's name, the relevant standard, and its classification code.
- Look for Third-Party Certifications: Approvals from recognized international bodies provide an additional layer of assurance that the product has been independently tested.
Following these steps ensures the conduits delivered to your site will meet local regulatory requirements, keeping your project on track.
Best Practices for Conduit Installation
Even the highest quality Class 4, hot-dip galvanized conduit is only as good as its installation. In the fast-paced construction environments of Dubai and Abu Dhabi, sloppy workmanship can lead to long-term failures. A professional installation is about understanding the why behind each step to build a robust, safe, and durable electrical pathway. Adhering to best practices, often with expert electrical installation services, is a direct investment in the system's longevity and safety, preventing costly rework and ensuring performance in the harsh GCC climate.
Proper Cutting and Deburring Techniques
The first step in any conduit run is cutting, but the most critical part is what comes next: deburring. After a cut, the inside edge of the GI electrical conduit will have sharp metal burrs that can shred wire insulation during pulling, creating a severe fire hazard from potential short circuits.
Crucial Tip: Always use a deburring tool or round file to smooth the inside of every cut. The rim should feel completely smooth to the touch before any cables are pulled. This simple check is a vital safety measure.
Secure Coupling and System Integrity
A conduit system's integrity depends on its connections. Proper use of couplings is non-negotiable for mechanical strength and electrical continuity.
- Threaded Couplings: For RMC and IMC, ensure threads are clean and tighten with a pipe wrench until "wrench-tight" to create a solid mechanical and electrical bond.
- Compression Fittings: For EMT, ensure the conduit is fully seated in the fitting before tightening the compression nut to prevent it from pulling loose under stress.
- Setscrew Fittings: Common for EMT, the setscrews must be tightened firmly to bite into the conduit wall, preventing loosening from vibration.
This same attention to detail applies to other containment systems. For more on this, see our guide on GI trunking installations.
Correct Bending Practices
Improper bending can kink or flatten a conduit, obstructing wire pulling and compromising its structural integrity. Always use a proper conduit bender designed for the specific size and type of conduit. Follow the bender's markings for clean, accurate angles without weakening the pipe. For large or parallel bends, a hydraulic bender offers superior precision.
Environmental Considerations for the UAE
Installing GI electrical conduits in the UAE and GCC requires specific techniques to combat the harsh climate.
1. Managing Thermal Expansion
Long, straight conduit runs exposed to the intense UAE sun will expand and contract, potentially causing buckling or loosening fittings. Expansion joints are the solution. These fittings accommodate movement without stressing the system. A good rule of thumb is to install an expansion joint for every 30 meters of straight conduit exposed to significant temperature fluctuations.
2. Sealing Against Dust and Moisture
Protecting electrical systems from dust and moisture is critical in this region. High IP-rated fittings, gaskets, and seals are essential.
- Ensure all junction boxes and enclosures have an appropriate IP rating (e.g., IP65 or higher) for their location.
- Use sealing locknuts or gaskets where connectors enter enclosures to create a dust-tight and water-resistant seal.
- In conduit runs passing between hot, humid areas and cooler, air-conditioned spaces, use a sealing compound (like "duct seal") to prevent condensation from damaging sensitive equipment.
By following these installation best practices, electricians and engineers can ensure a GI conduit system delivers on its promise of long-term protection and safety.
Maximizing Longevity Through Proper Maintenance
A quality GI electrical conduit system requires proactive maintenance to ensure it lasts for decades, especially in the demanding UAE climate. A structured maintenance plan is the key to ensuring long-term performance, protecting assets, and maintaining safety. A few scheduled checks can prevent catastrophic failures, spotting small issues before they become major expenses and keeping your electrical infrastructure reliable.

Developing A Proactive Inspection Schedule
Consistency is key to effective maintenance. A tiered inspection schedule is the most effective way to catch issues early.
- Quarterly Visual Checks (High-Risk Areas): For conduits exposed to harsh conditions (outdoor, coastal, industrial), perform a visual walk-through every three months to look for physical damage, surface rust, or loose supports.
- Bi-Annual Detailed Inspections (All Areas): Twice a year, inspect all couplings and fittings to ensure they remain tight, especially in areas prone to vibration.
- Annual Continuity Testing: At least once a year, use testing equipment to verify the system's grounding continuity. This critical safety check confirms an unbroken path to ground, essential for fault protection.
Addressing Common Maintenance Issues
During inspections, you may encounter several common issues. Quick and effective remediation is key.
1. Treating Surface Corrosion
Even hot-dip galvanized conduits can be scratched during installation. If surface rust appears:
- Use a wire brush to clean the area and remove all loose rust.
- Apply a coat of zinc-rich cold galvanizing spray or paint to restore the protective layer and halt corrosion.
2. Verifying Grounding and Bonding
Vibration or thermal cycling can loosen threaded connections or bonding jumpers over time.
A compromised ground path is a serious safety hazard. During annual checks, use a multimeter or a dedicated low-resistance ohmmeter to test the continuity between the start of the run and its connection to the main grounding system. The resistance should be exceptionally low, confirming a solid electrical bond.
3. Checking Supports and Fittings
Ensure all conduit straps, clamps, and supports are secure. A sagging conduit run puts stress on couplings and junction boxes. Tighten any loose hardware and replace damaged supports immediately.
The best maintenance plan begins with proper selection. Choosing a high-quality, hot-dip galvanized GI electrical conduit from the outset—especially for harsh outdoor or corrosive environments in Dubai and the GCC—gives you a significant advantage. Paired with a proactive inspection plan, this ensures your electrical raceway system delivers maximum safety and longevity.
Why Quality GI Conduits Are a Strategic Investment
Viewing high-quality GI electrical conduits as a mere line-item cost is a common mistake with serious long-term consequences. For procurement teams and project managers in the UAE and GCC, it is vital to recognize this as a strategic investment in a project's future—one that delivers returns long after completion. This perspective connects superior materials to tangible business outcomes, such as improved operational uptime and reduced risk of costly failures.
The Business Case for Superior Protection
While cheaper, non-certified conduits may offer upfront savings, this ignores the total cost of ownership. The real costs emerge later in the form of high maintenance fees, operational downtime, or even complete system replacement. In contrast, investing in certified, high-grade GI electrical conduits provides a clear financial advantage.
Here's how the business case breaks down:
- Slash Maintenance Overheads: Premium hot-dip galvanized conduits are designed to withstand the GCC's harsh climates. Their superior corrosion resistance drastically reduces spending on rust remediation and component replacement.
- Massively Reduce Operational Risk: An electrical failure can shut down a commercial tower, industrial plant, or data center. The financial impact of such downtime far outweighs the initial cost of quality conduits. This makes them a key part of your energy management solution Dubai strategy.
- Boost Project Reputation: Consistently delivering projects with high-quality, compliant components builds a solid reputation, leading to increased client trust, repeat business, and a stronger position in the competitive UAE construction market.
A project's electrical infrastructure is its operational lifeline. Investing in its protection isn't an expense—it's a core strategy for safeguarding long-term asset value and ensuring unwavering reliability.
The Growing Market Demands Quality
Market data underscores this reality. The electrical conduit market in the Middle East and Africa, valued at USD 450.72 million in 2023, is projected to reach nearly USD 636 million by 2032. This growth, driven by investments in real estate, industry, and renewable energy, highlights a clear demand for durable, high-performance components. For more details, see the analysis in this detailed Credence Research report. Rigid metallic conduits like GI dominate this market because they are designed to handle the region’s mechanical stresses and environmental challenges.
Partnering for Long-Term Success
Your choice of supplier is as critical as the product itself. Partnering with a knowledgeable provider like GoSwitchgear gives you more than just materials; you gain access to technical expertise and a supply chain dedicated to delivering certified products tailored for the unique challenges of Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and the broader GCC. This ensures you build an electrical system you can rely on for years to come.
Common Questions About GI Conduits
When specifying materials for major electrical projects in the UAE and GCC, there is no margin for error. We frequently address specific questions from engineers, electricians, and procurement managers about GI electrical conduits. Here are some of the most common ones.
Can GI Conduits Be Used Underground?
Yes, but with a critical requirement: for direct burial in soil or concrete, you must use hot-dip galvanized (HDG) Class 4 conduits. The HDG process creates a thick zinc coating that provides the heavy-duty corrosion protection necessary to withstand constant moisture and aggressive soil chemicals. Using pre-galvanised or Class 3 conduits for underground applications will lead to rapid corrosion and system failure.
What Is The Difference Between GI And PVC Conduits?
The key difference is the material and its intended application.
- GI Conduits (Galvanised Iron): These steel conduits provide superior mechanical strength and impact resistance. They are used in demanding environments like industrial plants, commercial buildings, and exposed outdoor runs where physical protection is paramount. They also serve as a grounding path.
- PVC Conduits (Polyvinyl Chloride): These non-metallic conduits are inherently corrosion-proof and lightweight. They are ideal for installations where physical damage is not a concern, such as within walls or in highly corrosive environments where even galvanized steel may degrade over time.
Do I Need Expansion Joints For GI Conduit Runs In The UAE?
Absolutely. This is a necessity, not a recommendation. The significant temperature swings in the GCC cause long, straight runs of steel conduit to expand and contract. Without accommodation for this movement, the conduit can buckle, bend, or pull apart from fittings.
As a rule of thumb, for any straight conduit run longer than 30 metres exposed to the sun or major temperature changes, installing expansion joints is non-negotiable. It’s a simple step that prevents serious mechanical stress and protects your installation for the long haul.
How Can I Verify A Conduit Meets BS 4568 Or BS EN 61386 Standards?
Verifying compliance is crucial for project approval and safety. There are two primary methods:
First, always request a Certificate of Conformity from your supplier. This official document from the manufacturer guarantees the product has been tested and meets the specified standard.
Second, inspect the conduit itself. Compliant GI electrical conduits will have permanent markings stamped or printed on them, clearly indicating the manufacturer's name, the standard (e.g., BS EN 61386), and its classification codes. When you source from a trusted supplier like GoSwitchgear, you are assured of receiving fully certified and correctly marked products.
For expert help choosing the right certified conduits for your projects in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, or anywhere in the GCC, check out the wide selection at GoSwitchgear.
Discover our full range of electrical components at GoSwitchgear










Leave a Reply